In recent years, blockchain technology has made great progress and has the potential to revolutionise several industries. From $6.6 billion in 2021 to around $12 billion in 2022, investments in blockchain technologies increased dramatically. With the potential to save banks over $10 billion annually, this technology has the potential to cut operational expenses by about 30%.
The need for blockchain architects is growing, and here’s why: As companies consider adopting blockchain technology, they want talented architects to design the networks, applications, and systems that run on it.
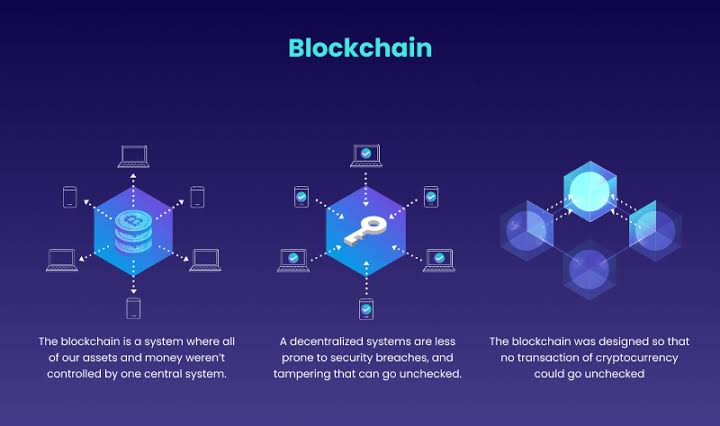
Due to its unique method of safely storing and transparently distributing data decentralizedly, blockchain stands out as a disruptive force. Blockchain uses a distributed ledger instead of conventional centralised systems that are vulnerable to hacks and single points of failure.
This makes it extremely impossible for any single entity to tamper with the data because numerous network nodes retain identical copies of the ledger.
The immutability of blockchain is a crucial aspect that makes it disruptive. Data cannot be changed or removed after it has been stored on the blockchain. Strong cryptographic methods enable this, making data extremely impossible to attack without network consensus. In addition, blockchain provides high auditability and transparency, making it a great tool for monitoring data movement and avoiding fraud. Its use in supply chain management, finance, healthcare, and other fields has resulted from this.
The potential of blockchain is far greater. Peer-to-peer transactions without a centralised authority are made possible by its ability to do away with intermediaries and drastically lower transaction costs.
Blockchain architects are in high demand because of these benefits. They are crucial in influencing the future of many businesses since they have a special skill set for designing blockchain-based solutions that fully use this technology.
In this article we’ll talk about who a blockchain architect is, roles and responsibilities of blockchain architect and the essential skills needed to become a blockchain architect
Who is a Blockchain Architect?
A Blockchain Architect is a specialist who plays a crucial role in creating Blockchain-powered solutions that are specifically adapted to the requirements of businesses and organisations. Their knowledge is crucial for applying Blockchain technology in numerous industries like supply chain management, healthcare, and finance.
A Blockchain Architect’s main goal is to make sure that Blockchain-based solutions are secure, effective, and scalable while also adhering to the unique needs of the organisation.
The architectural design and development of blockchain systems are carried out by these experts. Conceptualising and executing blockchain solutions that improve organisational operations and protect data are their primary responsibilities.
Blockchain Architects supervise the development of smart contracts, decentralised applications, and other cutting-edge solutions based on blockchain technology while working closely with a group of developers.
They are essential in identifying and resolving any technological issues that arise during the installation of a blockchain. They also stay up to date with the most recent developments and trends in the dynamic field of blockchain technology.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Blockchain Architect
A variety of crucial duties are included in the diverse work of a blockchain architect. They are given the responsibility of creating the technical architecture of Blockchain-based solutions, which necessitates a thorough knowledge of Blockchain technology.
This covers understanding of cryptography, smart contracts, consensus techniques, and distributed ledgers. Their capacity to appreciate the unique requirements of an organisation and how Blockchain technology may smoothly integrate into current processes, boosting efficiency and security, is equally crucial.
The responsibilities of a Blockchain Architect span various domains including:
1.They take the lead in creating safe, scalable Blockchain systems and carefully coordinating their design, development, and implementation with client needs.
2.Another crucial component of their duty is to investigate and assess new Blockchain technology. They offer suggestions for putting these innovative concepts into practise.
3.They are responsible for developing technical requirements and system architectures.
4.In addition to designing, they create decentralised applications, smart contracts, and Blockchain applications.
5.Their knowledge includes examining current enterprise systems and developing Blockchain-based solutions to improve security and speed up operations.
6.It is a continuous duty to maintain and watch over Blockchain-based systems to guarantee top functioning.
7.To enable the successful integration of Blockchain technologies, good cross-functional teamwork is essential.
These abilities are crucial for maximising the potential of Blockchain technology, particularly in light of the idea of a decentralised internet. The distinctive characteristics of blockchain, such as immutability, decentralisation, security, and transparency, make it a disruptive force in many industries.
Essential Skills Required for Blockchain Architects
One needs to have certain skills in order to succeed as a blockchain architect. These abilities are essential for handling the duties related to this employment. Let’s explore the important competencies you’ll require for success as you set out on your road to become a blockchain architect.
1. Establishing a Firm Foundation for Blockchain Architecture: It’s crucial to begin with the basics if you want to launch a prosperous career as a blockchain solution architect. The fundamental ideas of blockchain technology and its underlying architecture are covered in-depth in this. Distributed ledger technology, which serves as the cornerstone of this ground-breaking sector, is at the core of blockchain technology.
Having a solid understanding of distributed systems and peer-to-peer networking is essential to comprehending blockchain design. One must emphasise the distributed aspect of blockchain when answering the question, “What does a blockchain architect do?” Architects must have a thorough understanding of how distributed systems work and how network nodes communicate with one another.
It’s also critical to understand how blockchain overcomes the weaknesses brought on by single points of failure. In the process of learning blockchain architecture, this component is crucial.
2.Learning the Art of Programming Smart Contracts: Smart contracts, which are crucial to the blockchain ecosystem, are a core competency for blockchain solution architects. People frequently ask, “What coding skills are required for blockchain jobs?” The overwhelming reaction always points them in the direction of smart contract programming languages, with Solidity emerging as the top option.
By utilising the powerful capabilities of blockchain technology across many applications, smart contracts represent distinctive enhancements to blockchain networks. Understanding the inner workings of smart contracts and their intrinsic value becomes crucial for blockchain architects.
3.proficiency in development and programming: Programming and development know-how are at the top of the list of abilities needed for blockchain architects. But why is it essential for an architect to have programming knowledge? Let’s examine the role that programming knowledge plays in blockchain architecture.
The ability to programme effectively is essential for creating effective designs that flow naturally with programming languages.
Writing code is only one aspect of programming skills; another is comprehending the underlying logic of the architecture of blockchain solutions. You gain the information necessary to develop the best logical structure for your blockchain initiatives.
Another benefit of knowing how to programme is that you can implement your ideas for blockchain architecture. Your conceptualizations can be effectively translated into real-world blockchain applications and solutions.
4.Blockchain Security Foundations and Cryptography: Due to its strong cryptographic algorithms, blockchain technology has become well known for its abilities to improve security. Blockchain technology is built on the fundamental and extremely valuable component of cryptography. It takes a lot of work to protect a breakthrough technology from possible attackers, though.
Applications, protocols, and networks built on blockchains must all prioritise security. It’s a startling fact that security events in the blockchain industry have a financial impact that can reach billions of dollars annually. In order to strengthen blockchain security, a blockchain architect’s skill set must include knowledge of how to adopt best practises.
Additionally, while talking about the in-demand blockchain skills for architects, the focus invariably shifts to proficiency in smart contracts and blockchain security assessments. A blockchain architect’s resume might make a strong case for their aptitude for analysing blockchain solution code. In the face of potential attacks, this thorough examination guarantees the resilience and integrity of blockchain systems.
In conclusion, a Blockchain Architect plays a key and active position in the blockchain technology industry. The need for people knowledgeable in blockchain architecture is always increasing as a result of the rapid advancement of digital technology.
Blockchain architects are the brains behind scalable, secure, and efficient blockchain solutions that have the power to transform whole sectors. To negotiate the complexities of this game-changing technology, they must be proficient in a wide range of skills, including programming, cryptography, and interoperability.