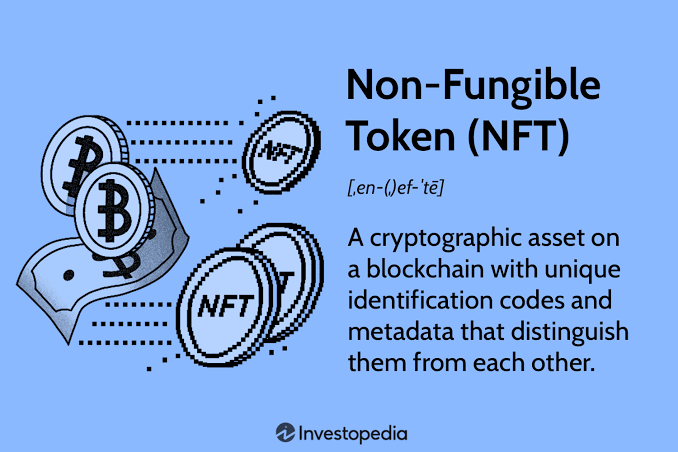
What is an Nft?
NFTs, also known as non-fungible tokens, are data units that are kept on the Blockchain. They have a unique code and can be used to represent digital media, allowing you to genuinely own a digital work of art. Digital media can take numerous forms, including video or music files, GIFs, tweets, and, of course, digital art. The crucial thing to understand is that, unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, NFTs are non-fungible, which means that each NFT is unique. They can be bought and sold, but they cannot be duplicated or copied, making them unique.
Before NFTs, digital art was frequently replicated, making it nearly hard to distinguish an original file from a clone. Digital artworks can now be identified, validated, and safely preserved on and off the internet using NFT and Blockchain technologies. It is simple and convenient to differentiate them from duplicates. This allows artists to monetize their digitised artworks by selling original or limited edition prints.
NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, have been making waves in the digital art industry. They not only help creators to commercialise their digital works, but they also give collectors with a new level of verification and scarcity. The adoption of blockchain technology enables NFTs to be one-of-a-kind, verifiable assets that cannot be copied or counterfeited.
NFTs provide creators with a new revenue source for their digital works. They can offer their pieces as one-of-a-kind assets rather than just digital data. This increases the possibility for creators to receive a larger return on their investment and for their creations to be more valuable. Furthermore, because NFTs can incorporate terms and conditions, creators can retain control over their creations and how they are used, which they include terms and conditions in their smart contracts.
NFTs offer a new degree of authenticity and scarcity to collectors. They can be certain that they have a one-of-a-kind piece of digital art that is not a reproduction. NFTs also enable the development of digital art collections that can be traced and authenticated on the blockchain.
Another benefit of NFTs in the art market is that they allow more people to participate. Because NFTs can be purchased and traded on the blockchain, anyone with an internet connection can participate. This broadens access to the art market and allows a broader range of people to participate.
Meanwhile, in this article we’ll discuss extensively about Non-fungible token, Nft boom and it’s varying effects on art market, as well as long term implications of Nft for Artists, collectors and investors
Nft boom and it’s effect on Art market
The rising popularity of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has opened up a new world of digital art and collectibles investing. NFTs are one-of-a-kind digital assets that are stored on a blockchain and serve as proof of ownership and authenticity.
The introduction of Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and digital collectibles has significantly disrupted the traditional art market, creating new opportunities and difficulties. NFTs have gained popularity, with artists, collectors, and investors flocking to this unique technology. This article investigates the effects of NFTs and digital collectibles on the art market, focusing on the effects on artists, collectors, and the wider industrial landscape. The following are the effects of Nft on Art market, they are as follows;
1.The Art Market’s Democratisation: Access to the art market has become more accessible and diversified as a result of NFTs and digital collectibles. The traditional art market was dominated by a small number of galleries, auction houses, and collectors prior to the development of NFTs. Artists can use NFTs to tokenize their digital artwork and sell it directly to collectors without the use of intermediaries. This has given a new generation of artists and collectors a global platform to promote and acquire art.
2.New Artistic Mediums Emerge: NFTs and digital collectibles have fueled the development and acceptance of new artistic forms like as digital paintings, animations, and virtual reality installations. These digital forms of art provide up new avenues for creativity and expression, allowing artists to experiment with new techniques and reach new audiences. The increased interest in digital art has also resulted in an increase in collaboration between artists and engineers, further accelerating the development of new artistic forms.
3 New Revenue Streams for Artists: NFTs have provided artists with new cash sources, allowing them to capitalise on the value of their digital compositions. Artists can be paid royalties when their work is resold in the secondary market using smart contracts. This provides a steady income source and motivates artists to continue creating creative and compelling artwork.
4.Decentralization: The decentralised nature of blockchain technology, which supports NFTs, has undermined the centralised structure of the traditional art market. Decentralisation provides artists and collectors with greater transparency and control by minimising the influence of strong intermediaries such as galleries, dealers, and auction houses. By allowing artists more control over the sale and dissemination of their work, this decentralisation has the potential to democratise the art industry and empower them.
5.Digital Ownership and Provenance: NFTs have introduced a new level of digital ownership and provenance to the art market. Each NFT is a one-of-a-kind, indivisible token that signifies ownership of a digital asset. This enables the secure tracking of provenance, allowing collectors to reliably check the authenticity and history of their acquisitions. The transparency enabled by blockchain technology has increased trust in the art industry, minimising cases of forgery and fraud.
6. Traditional Art Cross-Pollination: The advent of NFTs and digital collectibles has fueled interest in combining digital and traditional art forms. Collaborations between digital and traditional artists are increasing, as is the production of hybrid artworks that blend physical and digital aspects. This convergence of mediums is broadening the scope of artistic expression and attracting new audiences to the art industry.
7.The Rise of Digital Collectibles: Digital treasures such as virtual sneakers, in-game objects, and digital trading cards have also acquired appeal in the NFT industry. These digital assets have become incredibly valuable commodities, with collectors willing to pay enormous sums for rare and exclusive things. This has extended the reach of the art market, attracting new collectors and fans who might not have previously engaged with traditional forms of art.
8.Market Volatility and Speculation:The rapid rise of the NFT sector has raised worries about market instability and speculative behaviour. Critics worry that the surge of investors looking for quick returns could lead to price bubbles and harm the long-term worth of NFTs and digital collectibles. However, as the market grows, it is envisaged that true collectors and aficionados will continue to drive demand for high-quality digital art.
Long term implications of Nft for Artists, Collectors and Investors
Non-fungible tokens, often known as NFTs, are digital assets that enable the ownership and provenance of digital art and other online resources to be confirmed on a Blockchain. In recent years, the usage of NFTs in the art world has gotten a lot of attention as a mechanism for artists to sell their digital works and collectors to buy and own one-of-a-kind digital goods. NFTs will undoubtedly become an increasingly vital component of the art industry and the larger creative economy as their popularity grows.
NFTs have upended the traditional art world by providing new avenues for artists to commercialise their digital works. Artists can establish ownership and get royalties when their artwork is resold on the secondary market by selling NFTs of their work. This has the potential to completely transform the art market, which has traditionally been dominated by galleries and auction houses that take a large fee on sales.
The future of NFTs in the art world is still uncertain, but many experts believe they will continue to play an essential part in the industry. As more artists, investors and collectors become acquainted with NFTs, we should expect to see new and imaginative use of them in the art world. Some possibilities include the establishment of virtual art exhibitions, interactive digital art installations, and even augmented reality experiences.
NFTs also provide collectors with a unique method to invest in art while simultaneously supporting their favourite artists. Collectors can own a piece of digital art that is certified on the blockchain and easily transferrable by acquiring NFTs. This offers up a whole new market for art collectors who may not be able to afford tangible artworks or want to acquire digitally. NFTs also allow large investors to participate with the assumption that the value of the non-fungible token will rise in the near future.
However, there are concerns regarding the environmental impact of NFTs, as the energy required to mine and store blockchain data is enormous. To ensure the long-term survival of NFTs in the art world, the industry must discover more sustainable ways to use blockchain technology.
Conclusively, NFTs have already had a substantial impact on the art world by creating new ways for artists, investors, and collectors to commercialise and invest in digital art. While there are still obstacles to overcome, the future of NFTs in the art world appears promising, with limitless opportunities for creativity and expansion.