A distributed network ensures that multiple peers are accessible to accept and authorise a transaction in a decentralised platform, whether that transaction is saving or processing a file or transmitting bitcoin to your other peer. Even if some verifiers were unavailable on the network, you don’t have to wait for the transaction to be verified. Users can use a blockchain wallet to transfer, receive, store, and exchange value on the blockchain, as well as monitor and control the value of their assets.
A blockchain network allows scattered users to not only communicate directly with one another but also to transact value with one another. All of this occurs without the use of a middleman or a single point of failure and in a secure manner thanks to the benefits of cryptography. When the requirement for trust through human verification is eliminated or limited, peer-to-peer transactions and communications offer cheap cost and high speed.
When it comes to avoiding a single point of failure, if you submit a transaction to the other person through a bank, you must wait for the transaction to be manually or automatically verified. If a banking service is unavailable due to internal or external circumstances, you will be unable to transact and will have to wait.
What is a Blockchain Wallet?
A blockchain wallet is a piece of digital software that holds private and public keys, as well as monitors and records all transactions involving those keys on the blockchain. A blockchain wallet, in theory, does not store cryptocurrency; instead, all records pertaining to these keys are maintained on the blockchain on which the wallet is housed.
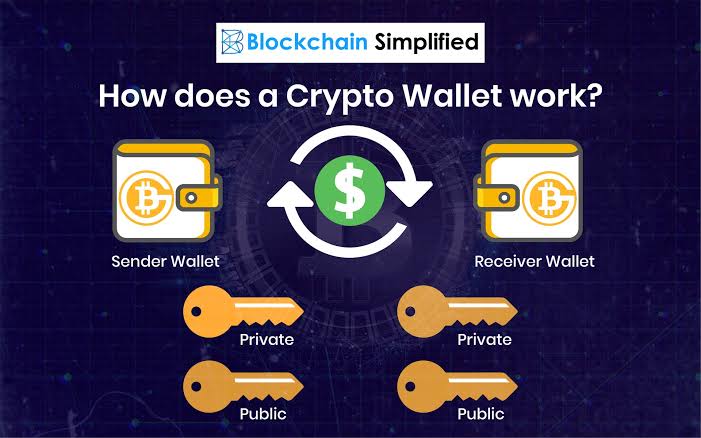
What this implies is that the wallet generates an ID that can be used to track all transactions related to it. The blockchain wallet address, which is linked to the public and private keys, is the blockchain ID.
Blockchain wallets, in practice, allow users to store, send, receive, and manage digital assets such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and other cryptocurrencies on the blockchain.
A blockchain wallet makes it simple to transfer money. Because transactions are cryptographically signed, they are safe. The wallet may be accessed from any online device, including mobile devices, and the user’s privacy and identity are protected. As a result, a blockchain wallet includes all of the characteristics required for safe and secure fund transfers and swaps between participants.
How Do Blockchain Wallets Work?
A unique master seed is created when you create your Blockchain Wallet. This master seed is the foundation of your wallet, and it’s used to generate each bitcoin address you’ll use to send and request bitcoin.
Wallets do not keep your bitcoins; instead, they supply you with the software necessary to do so. Your personal password is used to encrypt your wallet on your device. This is known as client-side encryption, and it means that your wallet is only accessible to you. Your password serves as the decryption key for both locking and unlocking your wallet; without it, you won’t be able to access it. Because wallets don’t know or save your password and can’t reset it, the only way to unlock and decrypt your wallet is for you to do it.
Your encrypted wallet is backed up to the servers of your wallet service provider automatically. Another degree of security is given by encrypting your wallet a second time to keep it safe. By securely storing your wallet on the servers, you’ll be able to access it from any (and all) of your devices. Your browser uses the wallet service provider’s API to download your encrypted wallet backup before safely decrypting it on your device when you access your wallet with your Wallet ID (a unique identifier particular to your wallet) and password.
Your Backup Phrase is an encoded version of your master seed made up of 12 random words (and it is industry-standard). It serves as a backup and allows you to access your bitcoins and ether regardless of your wallet software. If you forget your password or switch to another wallet service provider, your Backup Phrase is all you’ll need to get back into your money.
Types of Blockchain Wallet
Hot wallets and cold wallets are the two types of blockchain wallets based on private keys. Hot wallets are similar to the wallets we use for everyday transactions, and they are user-friendly. Cold wallets are similar to vaults in that they hold cryptocurrency in a secure manner.
Hot Wallets
A hot wallet is a cryptocurrency wallet that is always online and connected to the blockchain. Hot wallets are used to transmit and receive cryptocurrency, as well as to keep track of how many tokens you have. If you acquire or mine a cryptocurrency, you’ll need to create a wallet to make transactions easier if you want to use it to buy products or services. When the ecosystem transfers ownership to you, your cryptocurrencies, or rather the private keys you use to access the money, are held in these wallets.
When you purchase a cryptocurrency, you are given private keys that allow you to identify it as your own. Public keys are similar to account usernames in that they identify the wallet and allow the user to get tokens without having to divulge their identity. Private keys are comparable to personal identification numbers in that they allow you to access your wallet and perform functions such as checking balances, initiating transactions, and so on. The wallet is effectively useless without one of these keys.
Hot wallets are internet-connected applications that link to the cryptocurrency infrastructure and allow you to use them. A user’s hot wallet is the interface via which they can access and store their cryptocurrency. Their job is to make any changes to the transaction record stored on the decentralised blockchain ledger for any cryptocurrency you’re using easier for the cryptocurrency network.
Cold Wallets
A cold wallet, commonly referred to as cold storage, is an offline wallet for holding bitcoins or other cryptocurrencies. The digital wallet is stored in cold storage on a platform that is not linked to the internet, protecting it against unauthorised access, cyber hacks, and other vulnerabilities that a system connected to the internet is vulnerable to.
An offline wallet for storing bitcoins or other cryptocurrencies is known as cold storage. The digital wallet is stored in cold storage on a platform that is not linked to the internet, protecting it against unauthorised access, cyber hacks, and other vulnerabilities that a system connected to the internet is vulnerable to.
Conclusively, a blockchain wallet helps someone exchange funds easily. Transactions are secure, as they are cryptographically signed. The wallet is accessible from web devices, including mobile ones, and the privacy and identity of the user are maintained.